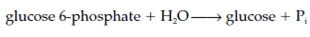Precursors for gluconeogenesis:
Glycerol can act as a substrate for glucose synthesis through conversion to dihydroxyacetone phosphate and an intermediate in gluconeogenesis. In order for citric acid cycle pyruvate, lactate, intermediates and the carbon skeletons of most amino acids to act as precursors for gluconeogenesis and these compounds must first be transformed to oxaloacetate. various of the carbon skeletons of the amino acids provide increase to oxaloacetate straightly. Others feed into the citric acid cycle as intermediates and the cycle then converts these molecules to oxaloacetate. Lactate is converted to pyruvate through the lactate dehydrogenase reaction and some amino acids also provide increase to pyruvate. Therefore, for these precursors the first step in the gluconeogenic pathway is the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
The steps in gluconeogenesis are as follows:
1. Pyruvate is converted to oxaloacetate through carboxylation using the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase which is situated in the mitochondrial matrix.
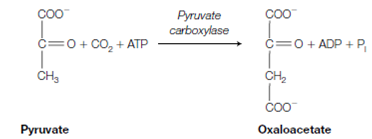
This enzyme uses biotin as an trigger carrier of CO2 the reaction occurring in two stages:
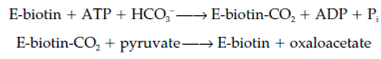
2. The oxaloacetate is now acted on through phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase that concurrently phosphorylates and decarboxylates it to form PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate), releasing CO2 and using GTP in the procedure:
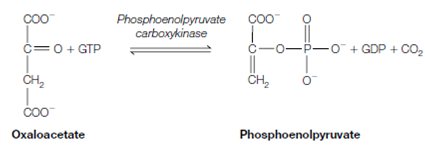
Therefore, reversal of the glycolytic step from PEP to pyruvate needs two reactions in gluconeogenesis, pyruvate to oxaloacetate through pyruvate carboxylase and oxaloacetate to PEP through PEP carboxykinase. Provide in which the conversion of PEP to pyruvate in glycolysis synthesizes ATP, it is not surprising which the whole reversal of this step required the input of a substantial amount of energy one ATP for the pyruvate carboxylase step and one GTP for the PEP carboxykinase step.
3. PEP is converted to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate in a series of steps which are a direct reversal of those in glycolysis by using the enzymes enolase, phosphoglycerate kinase, phosphoglycerate mutase, glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate triose, aldolase and dehydrogenase phosphate isomerase. This sequence of reactions uses one ATP and one NADH for every PEP molecule metabolized.
4. Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate is dephosphorylated to form fructose 6-phosphate through the enzyme fructose 1 and 6-bisphosphatase in the given reaction:
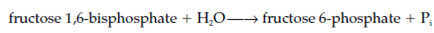
5. Fructose 6-phosphate is converted to glucose 6-phosphate through the glycolytic enzyme phosphoglucoisomerase.
6. Glucose 6-phosphate is converted to glucose through the enzyme glucose 6- phosphatase. That enzyme is bound to the smooth endoplasmic catalyzes and reticulum the reaction: