Nucleosomes:
The first stage of packaging includes the binding of the chromosomal DNA to histones. Whole, in chromosomes the ratio of the DNA to histones on a weight basis is around 1:1. There are five major types of histones known as H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Histones are very basic proteins; about 25 percent of their amino acids are lysine or arginine so histones have a huge number of positively charged amino acid side-chains. These positively charged groups thus bind to the negatively charged phosphate groups of DNA. Not surprisingly providing their importance in packaging DNA the amino acid series of histones have been highly conserved in evolution. The most preserved are histones H3 and H4; for instance, H3 and H4 from cows and peas differ in only four and two amino acids respectively! Histone H1 is the least conserved histone, that reflects its somewhat different role in packaging DNA compared with another histones. In sperm heads DNA is particularly highly condensed and here the histones are replaced with small basic proteins that are known as protamines.
When chromosomes are gently decondensed they have the appearance under the electron microscope of 'beads on a string'. The 'beads' are known as nucleosomes and consist of DNA complexed with histones. The string is linear double-stranded DNA among adjacent nucleosides and is known as linker DNA. The average distance among nucleosomes which is the length of the linker DNA is usually about 55 base pairs (bp) but varies greatly from organism to organism. Even in a single nucleus the distance among adjacent nucleosomes varies depending on, for instance, the presence of other sequence- exacts DNA-binding proteins if a chromatin preparation is incubated with micrococcal nuclease, an enzyme which degrades DNA the linker DNA is destroyed leaving nucleosome core particles in that the histones protect the related DNA from digestion. Every nucleosome core particle contains a
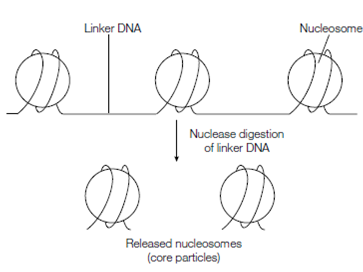
figure: 'Beads-on-a-string' structure of chromatin.
double-stranded DNA fragment 146 bp long bound to a complex of eight histones the histone octamer, consisting of two molecules every of histones H2A, H3, H2B and H4. The DNA is wound round the outside of the histone octamer in regarding 1.65 turns of a left-handed supercoil. DNA-histone contacts are made along the inside face of this superhelix. Whole the packing ratio is about 7 which is the DNA length is shortened about seven-fold through winding around the nucleosome.