Nuclear plants
As coal reserve is not limitless, there is natural threat to thermal power plants depend on coal. It is predictable that in next 30 to 40 years, coal reserve will exhaust when it is consumed at the current rate. Nuclear power plants are considered to be the answer for bulk power production. At current the installed capacity of nuclear power plant is around 4300 MW and predicted to expand further in our country. The current day atomic power plants work on the principle of nuclear fission of 235U. In the natural uranium, 235U comprises only 0.72% and remaining portion is comprised by 99.27% of 238U and only around 0.05% of 234U. The focus of 235U might be raised to 90% by gas diffusion procedure to acquire enriched 235U. Whenever 235U is bombarded by neutrons a lot of heat energy all along with additional neutrons is generated. Such new neutrons further bombard 235U generating more heat and more neutrons. Therefore a chain reaction sets up. Though this reaction is permitted to occur in a controlled manner within a closed chamber termed as nuclear reactor. To make sure sustainable chain reaction, moderator and control rods are employed.
Moderators like heavy water (i.e., deuterium) or very pure carbon 12C are employed to decrease the speed of neutrons. To control the number neutrons, control rods made up of cadmium or boron steel are inserted within the reactor. The control rods can soak up neutrons. When we want to reduce the number neutrons, the control rods are lower down further and vice-versa. The heat produced within the reactor is taken out of the chamber with the help of a coolant like liquid sodium or some gaseous fluids. The coolant gives the heat to water in heat exchanger to transform it to steam as shown in figure below. The steam then drives the turbo set and the exhaust steam from the turbine is cooled and fed back to the heat exchanger with the help of water feed pump. Evaluation illustrates that to generate 1000 MW of electrical power in coal based thermal plant, around 6 × 106 Kg of coal is to be burnt daily whereas for the similar quantity of power, only around 2.5 Kg of 235U is to be employed per day in a nuclear power stations.
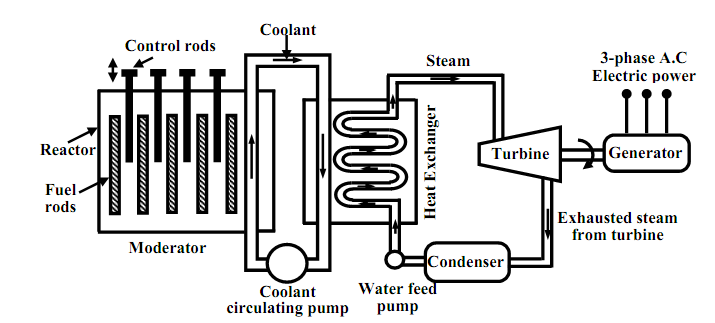
Figure: Nuclear power generation.
The primary investment needed to install a nuclear power station is quite high though running cost is low. However, nuclear plants generate electricity without causing air pollution; it stays a dormant source of radiation dangers due to leakage in the reactor. Also the used fuel rods are to be cautiously handled and disposed off as they still stay radioactive.
The reserve of 235U is also limited and can’t last longer when its consumption continues at the current rate. Naturally search for another fissionable material continues. For illustration, plutonium (239Pu) and (233U) are fissionable. However they are not directly available. Absorbing neutrons, 238U gets transformed to fissionable plutonium 239Pu in the atomic reactor explained above. The used fuel rods can be further processed to remove 239Pu from it indirectly rising the availability of fissionable fuel. Effort is also on to transform thorium into fissionable 233U.
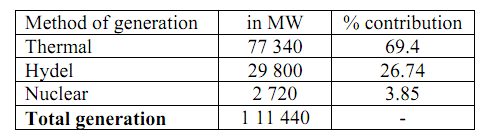
By the way, India has very large reserve of thorium in the world. Total estimated generation capacity and contribution by thermal, hydel and nuclear production in our country are shown below.