Description of the Economy:
Let us consider a pure exchange model where no production takes place. Consumers have initial bundles of goods, initial endowments. They exchange with each other these goods according to their preferences. For example, you have quantities of apples and 1 have oranges. We enter into an exchange, your apple and my oranges. Note that the exchange to take, you must be willing to consume my oranges and I am willing to consume your apples.
We can think of n consumers and k commodities in the economy. Each consumer has initial endowments and preferences. Whereas endowment refers to the commodity held by a consumer, her preferences are represented by a utility function y = u, 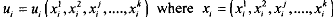 is the ith individual's consumption bundle.
is the ith individual's consumption bundle.
We introduce a price system P such that P = (PI, Pz, ...., Pk). Note that the economy you are presented with, does required payment terms of money as people trade one good for another (exchange in barter system). But the price we intend to use is for the exchange rates. For example, the price of one unit of good X is one unit good Y. Such a price, therefore, can be called relative price of good X. If the price of Potato is Rs. 5 per kg and the price of apple is Rs. 2.5 per kg, then the relative price of Potato in terms of apple is 2 (i.e., each unit of Potato is worth 2 units of apple). Similarly, the relative price of apples in terms of Potato is 0.5 (i.e., one unit of apple is worth half unit of Potato).
Remember that we will use relative price in the following analysis. Imagine that the consumer i purchases x,' units of good j at price PJ. Then PJ.X, gives the amount of expenditure incurred by her and to that extent her income stands reduced. On the other hand, when she delivers goods of equal quantity, the income t',x,' is added to her income.
To arrive at the equilibrium of the model, let us start with consumer's utility maximisation. See that the ith consumer maximises
Ui(Xi) subject to her budget constraint PXi = PWi. Remember that solution to this problem yields the demand functions Xi = X,(P, PWi), i =1,2,.. .n and demand for each commodity depends on all prices and the initial endowment.