Competitive equilibrium:
In selecting an economy with pure exchange, we ignore the production at this point of our analysis. Such a framework helps us concentrate on allocation of goods that are alrea4 produced. Our concern now is to find a criterion of allocation agreed to be 'good' enough by the society. The framework of social welfare in which we looked for Pareto efficiency in Block 5 is invoked to see that competitive equilibrium ensures that.
Edgeworth Box:
As we have already seen a useful graphical tool for describing the feasible allocations for the economy with 2 agents (A, B) and 2 goods (F, S) is the Edgeworth box.

The Edgeworth box combines the x-y axes of the two consumers such that when we allocate more to consumer A, there is less available for consumer B. Figure shows the Edgeworth box for this economy. All the allocations inside the box are feasible. However, the preferences do not depend on the set of feasible allocation.
Let us start with position E in the figure, which depicts the positions of A and B, with their initial endowments. If trade is allowed where will they end up? It is not clear because either or bath could be made better without making either worse off. However, we can say that they need to be somewhere in the lens shaped region between uA and uB. Why? Because all these points Pareto dominate E, where Paretodominate implies the following:
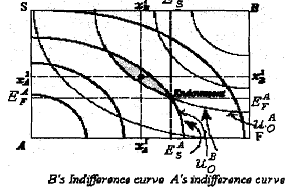
Consider two allocations x and x' . The allocation x' is said to Pareto dominate x if everyone prefers x' to x. In the figure one or both parties could be made better off without making the other worse off. Thus, there are potential gains from the trade.
Next, we look at the indifference curves of both consumers. We have assumed that the preferences are convex and increasing in both goods. Note that it is possible to make both consumers better off by moving them to allocation inside the lens area formed by the indifference curves. That is, if agents consume their initial endowments, then this allocation will not be efficient. On the other hand, if there is a possibility to make both consumers better off, there is no reason for not doing that. In the figure, equilibrium is determined at the point where the two IC's are tangent. Given the prices indicated by the slope of the price line, both agents maximise utility with respect to their budget set. Thus, at equilibrium, the MRS of the two agents are equal:
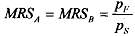
An important result that you have to remember is, in the equilibrium only the relative price matters.