Pitch Circle and Base Circle Radii
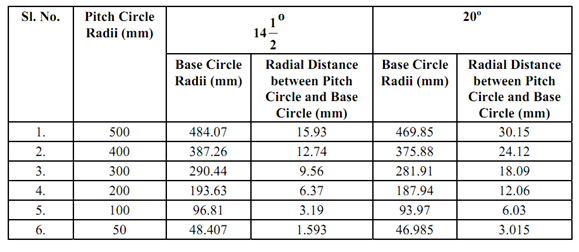
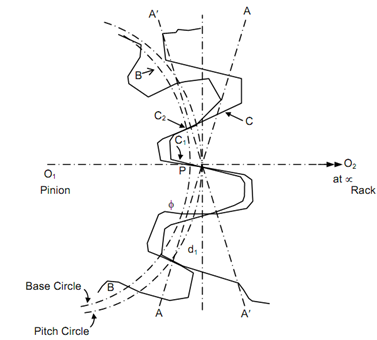
The following Table denote that the radial distance among base circle and pitch circle reduced. At one stage, a situation can reach that the radial distance among pitch circle and base circle becomes less than the needed standard dedendum for a pinion. As involutes do not persists below the base circle and in such a condition to provide standard dedendum, the tooth profile can be extended along radial line inside the base circle as it is normal line at the base circle. Such a pinion is illustrated in Figure meshing having an involutes rack. A′A′ is path of contact for contact with involutes profile and O1 and O2 is line of centres. BB is the base circle of pinion. Since the motion is transmitted, the rack tooth shall have area contact along radial flank of pinion tooth at C1 and C2 when making contact at P that is undesirable and the radial portion of flank shall not follow law of gearing. At any instantaneous, the portions of the tooth profiles that are in contact should be involutes so that the line of action does not deviate. As a consequence of these actions, pinion and rack will not result in appropriate transmission of power. Mating of two such non-conjugate teeth shall result in interference because teeth shall have rough action in transmission of motion.
Pitch Circle and Base Circle Radii