Current-voltage curve:
A fact detector is made up of conducting material along with an electrically isolated central wire. An extremely thin window made of mylar, aluminium or beryllium is given at one end of the detector that is filled along with a mixture of a primary gas (such as Ar, Kr, Xe termed as P gas) and a quenching gas (such as CH4, alcohol vapours or halogen gas like as Cl2). Alternatively a continuous flow of the gas (liquid petroleum gas is frequent used) could be sent through the chamber. Within that case, it is known as continuous flow proportional counter.
In the absence of any radiation there is no ion-pairs are formed and therefore no current passes through the tube. Therefore, while voltage is applied across the central wire and nuclear radiations enter the tube, ion pairs are formed and current passes. As voltage is rise the number of ion pairs formed increases. A plot of number of ion pairs created or ion current vs. voltage applied across the central wire is display in Figure.
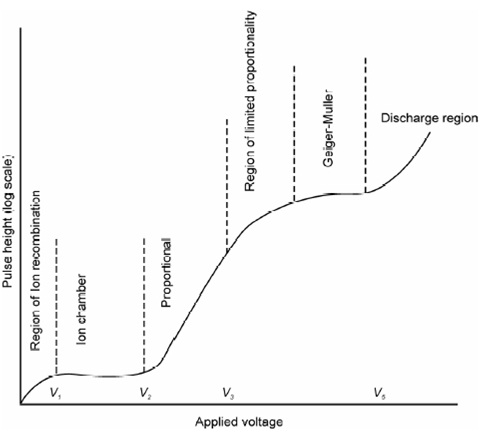
Figure: Typical current-voltage curve showing variation of pulse height as a function of applied voltage for a gas ionization detector