Total peak area calculation:
The superimposition of photo peaks on each other or the high Compton background makes it difficult to precisely determine the net counts in the region of interest (ROI). The base area is mostly taken as trapezoidal summation of the average counts in each channel giving the background over which the photo peak is situated as illustrated in Figure.
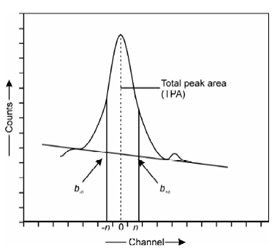
Figure: Illustration of activity calculation from total peak area calculation
For NAA, the most important of all the various factors mentioned above is peak area calculation. Typically peak area may be calculated as in Eq. (12.13), derived for single channel analyzer. However, while using MCA several methods have been proposed to determine the total peak area (TPA) represented as:
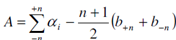
where, n = number of channels on right (+) and left (-) of the peak channel (o),
αi = total counts in i channels,
b±n = background counts in 2n channels as determined from a straight line drawn between the channels to left and right to peak channel.
Various software's has been developed whereby closely lying multiples can be resolved into individual photo peaks.