Galvanic Corrosion at Iron-Copper Pipe Junction:
Below figure describes that galvanic corrosion occurs while two different metals are within contact and exposed to an electrolyte.
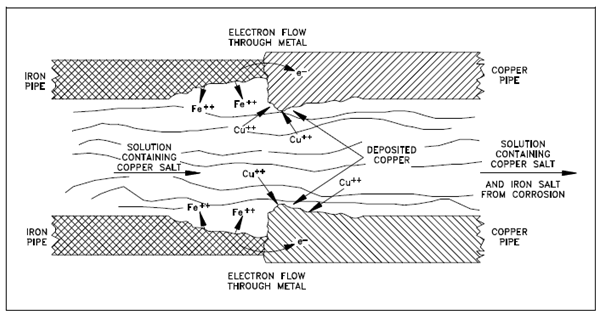
Figure: Galvanic Corrosion at Iron-Copper Pipe Junction
Figure displays the junction of iron and copper pipes holding a solution of a copper salt. The oxidation potential of iron is enough greater than that of copper so that iron is capable of reducing Cu+2 ions to copper metal. In that case, iron corrodes close the junction, and further copper builds up on the copper pipe near the junction.
The solution to that the metal junction is exposed required not hold a salt of one of the metals for galvanic corrosion to occur. The reduction reaction would be as shown in Equation if the iron-copper junction were exposed to water without Cu+2 ions.
H3O++ e- → H + H2O
Rapidly, iron would corrode near the junction, other than in this case hydrogen would be established on the surface of the copper.