Generation of the acylium ion:
Keeping this in mind how is it probable to make structures such as 1-butylbenzene in good yield? The reply to this problem lies in the Friedel-Crafts acylation. Through reacting benzene along with butanoyl chloride instead of 1-chlorobutane, the essential 4-C skeleton is connected to the aromatic ring and no rearrangement occurs. The carbonyl group can then be removed through reducing it with hydrogen over a palladium catalyst to provide the wanted product.
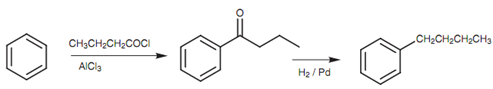
Figure: Synthesis of 1-butylbenzene by Friedel-Crafts acylation and reduction.
The mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts acylation is similar like the Friedel-Crafts alkylation involving an acylium ion in place of a carbocation. Since with the Friedel-Crafts alkylation, a Lewis acid is needed to generate the acylium ion (R-C= O)+, but not like a carbocation the acylium ion does not rearrange because there is resonance stabilization from the oxygen.
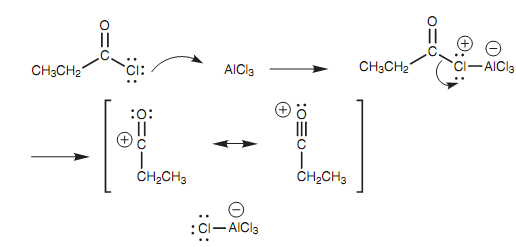
Diagram: Generation of the acylium ion.
Friedel-Crafts alkylations can as well be performed using alkenes instead of alkyl halides. ALewis acid is not needed, but a mineral acid is required.