Example of Area Subdivision Method:
The procedure shall be explained with respect to an illustrative problem illustrated in Figure (a), with the image consisting of five objects, namely a triangle (T), quadrilateral (Q), square (S), horizontal rectangle (H), and vertical rectangle (V). The viewport PQRS is 16 pixels by 16 pixels, having only part of the image. The square is behind the quadrilateral and the triangle and the two rectangles are in front of the quadrilateral.
For easiness of understanding, all five polygons are assumed to be parallel to the x-y plane, not intersecting one another. The same procedures may, however, be applied to handle the intersection of two polygons. Figure (a) illustrated the problem as presented; (b) is the pixel-wise representation of the polygon edges; (c) illustrated the external (disjoint) part of the quadrilateral clipped away.
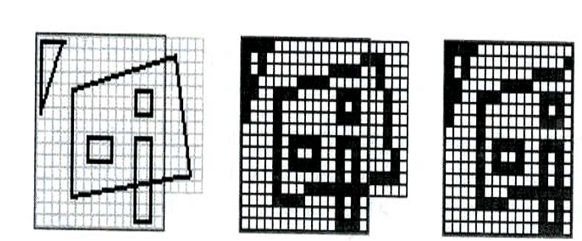
(a) (b) (c)
Figure: Subdivision Method Example : (a) Five Objects and Viewport; (b) Pixels Defining the Edges; and (c) External Portion Clipped
At the zero-th level, namely for the entire viewport, the only decision that may be made is that the x-y extent of the triangle does not intersect the extent of any of the other polygons, and therefore can be declared visible.
The subdivision of the viewport and further analysis are illustrated in Figure. In the figure, the z locations of the five objects are schematically indicated on the left, with T being closest to the viewer.