Mass Moment of Inertia of Flywheel for a Punching Press:
In this torque supplied is constant as these machines are driven through the electric motor however the demand torque, that means resisting torque varies throughout cycle. The instance of them is, shearing machine, punching press etc.
The schematic diagram of punching press is illustrated in Figure. In place of slider in slider crank mechanism punching tool is utilized. As motor is utilized to drive this press, the torque supplied will be constant. Alternatively, high resisting torque will behaves while punching operation is done, that is from θ = θ1 to θ2. After this operation the resisting torque shall be almost zero. Unless a flywheel is utilized, the speed of the crank shaft shall be very high while resisting torque is very little and substantial decrease in speed while punching operation is completed. If flywheel is provided, the excess energy will be absorbed in the flywheel and this shall be available while punching operation is being done while energy is deficient. This will result in reduction of the power of motor needed.
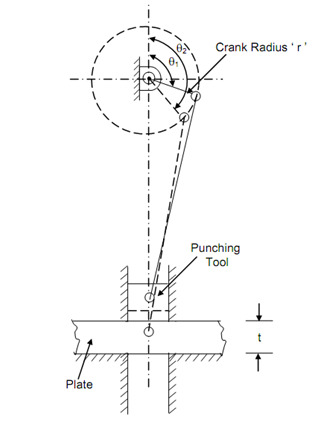
Assume E be the energy needed for punching one hole. For a constant operation the energy supplied to the crank for revolution must also be equivalent to E.
The fluctuation of energy 'Δ E' = Energy needed for one punch - Energy supplied throughout punching
Energy E = Work done in punching hole = {Maximum force/2 (P)} × Thickness
P = Sheared area × Shear strength
Energy supplied during punching = E (θ2 - θ1 ) / 2π
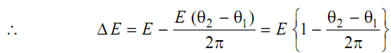
Angles θ1 and θ2 must also be in radians.
Assume t is the thickness of the plate in which holes are to be punched.
s is the length of the stroke.
r is the length of the crank.
l is the length of the connecting rod.
θ1 and θ2 may be determined geometrically if r, l and t are known.
The rough estimate can also be made as follows:
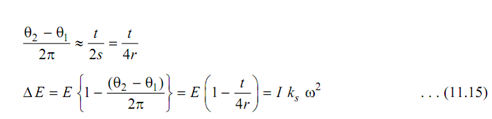
The mass moment of inertia of the flywheel for a specified value of coefficient of fluctuation of speed may be determined. To drop off the size of flywheel it shall be better to mount the flywheel on a shaft along higher value of 'ω'.