Analysis of Gaseous Pollutants:
The analysis of gaseous pollutants is totally based on the phenomenon of chemiluminescence. We start with the determination of NO - NO2 as atmospheric pollutants. The principle of like a determination is discussed here. The procedural details could be found in the laboratory manuals or from the manuals of pollution control agencies.
Determination of NO - NO2
In order to determine the amount of NO, the gas is passed by the reactor in which it reacts with ozone. Initially the excited NO* species is produced as per the reaction given below.
NO + O3 ↔ NO* + O2
The activated NO* then provides chemiluminescence broadband within the visible to infrared range (600 - 2800 nm) and reverts back to a lower energy state. The emitted photons are proportional to the amount of NO present and are measured along with the help of a photomultiplier tube (PMT).
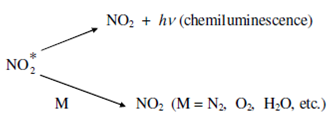
The presence of other species, M contributes towards nonradiative deactivation. The intensity of the emitted radiation (I) is given through the following equation:
I = Constant × [NO] [O3] [M]-1
The luminescence intensity is found to be straight proportioned to the concentration of MO, O3 and is inversely related to the other species, M.