Determination of blood glucose:
The determination of blood glucose is based on the subsequent reactions.
Step 1: A enzyme glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of β-D-glucose to form D-glucono-1,5-lactone and hydrogen peroxide.

Step 2: D-glucono-1, 5-lactone after that spontaneously gets hydrolysed to produce gluconic acid.
D-Glucono-1,5 -lactone +H2O → D-Gluconic acid
As the α -D-glucose is rapidly converted to the beta form, thus, all of the glucose is measured at a single time. This glucose oxidase catalysed reaction could be monitored through fluorescent detection of the consumption of oxygen or through monitoring the production of hydrogen peroxide. An amount of hydrogen peroxide generates is determined through using a fluorophore named luminol.
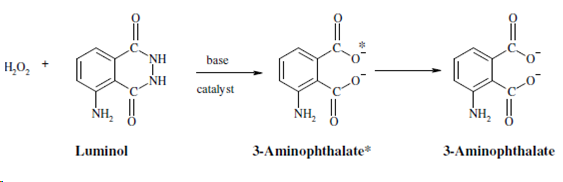
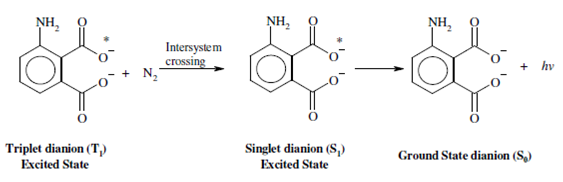
The detection limit of glucose through this method is 50 µg/ml. This reaction could be used for analysis of fructose or sucrose also. Presently some biosensors are also being established to measure blood glucose stages. These biosensors are based on sensitive fluorescence measurements that work through monitoring changes within the intrinsic FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) fluorescence of glucose oxidase. FAD is the cofactor of the enzyme.