Flying of an Aeroplane:
Do you know how an aeroplane lift itself above the ground and keep flying in the air? It is majorly because of the aerodynamic force called lift. To understand the operation of the lift force, we need to apply the Bernoulli's equation on the air (fluid) around the wings of the aeroplane. Refer to Figure which shows the cross-section of the wing of an aeroplane. When the airplane moves, the air above and below the wings flow. Aeroplane wings are so designed (i.e. streamlined) that the total distance traveled by air flowing over the wing is longer than that of the distance under it. Thus, the velocity of air flow above the wing must be higher than the velocity of air flow under the wing. Now, according to Bernoulli's equation, in this situation, the pressure p2 above the wing must be lower than the corresponding pressure p1 under the wing. This unbalanced in pressures causes a force (lift) to act on the wings. The lift force can be resolved into two components - the vertical component, L enables the aeroplane to rise above the ground and the horizontal component, D (also called drift) enables it to keep flying in the air.
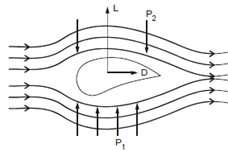
Figure: Air Pressures in the Upper and Lower Regions of the Wing of an Aeroplane
Till now, you studied the dynamical properties of non-viscous fluids, that is, the characteristics of the frictionless fluid motion. However, the motion of real fluids is opposed by frictional or viscous forces. This characteristic of fluids to resist motion is known as viscosity about which you will learn now.