Flow-of-Funds Accounts:
The flow-of-funds accounts are the financial counterparts of the national income accounts of the real sector of the economy. These provide a systematic way of integrating saving, investment, lending, and borrowing. In so doing, it brings together the real and financial sectors of the economy. For these reasons, an understanding of the flow of funds accounts is an indispensable tool of the financial analyst.
What are flow-of-funds accounts? The flow-of-fund accounts include all the sources and uses of funds for the various sectors of the economy, and by summation, for all sectors.
Although aggregate saving and investment must be equal, ex post, for the entire economy, it is unlikely that saving will equal investment for a particular sector during a given period. Saving may exceed investment; the surplus on current account will have been used for purposes other than financing current expenditures. For example, the surplus funds may have been used to buy securities or to take loans. If a sector has investment greater than saving, sources other than its own saving will have provided the funds necessary to finance these expenditures. Thus, saving is but one source of funds; investment is but one use of funds.
Data for Flow-of-Funds Accounts Flow of funds data for an economy are derived for a specific period of time by (1) dividing the economy into sectors, (2) preparing a source and use of funds statement for each sector, (3) summing the sources and uses for all sectors, and (4) placing the sector accounts side by side to form a table or matrix.
A matrix may consist of only a few sectors. For example, the entire economy can be divided into households, business firms, governments and financial institutions. In a more complex matrix, these sectors may be subdivided with additional categories established for different types of business firms, government units, financial institutions, and so on. And if foreign transactions are to be considered, it is necessary to include a sector for the rest of the world. The larger the number of sectors, the more likely it is that each sector will be composed of relatively homogeneous units. Ideally, each group's market behaviours will be similarly influenced by the same set of economic variables. However, if the economy is divided into too many sectors, the model becomes cumbersome, so too much detail may obscure more important relationships between them. The optimum number of groups depends ultimately on the purpose of the analysis and the degree of disaggregation necessary, on the availability of data, and on the time and effort required to collect and assemble the date.
The second step in construction of flow of funds accounts is to prepare a source and use statement for each sector. This is done by examining the balances sheets of the various sectors at the beginning and end of a quarter or a year. Net changes are noted in the stock of assets, liabilities, and net worth that occurred during the period. Certain assets might have increased in value, others declines: some liabilities may be greater and some smaller than at the beginning of the period. The convention is to treat increases in assets as a use of funds and increases in liabilities or net worth as a source of funds. On the users side, the sum of the changes in real and financial assets must be equal to, on the sources side to change in liabilities and change in net worth.
A simple source and use statement for a given sector shows intersectoral flows on a new basis. That is, it does not record intersector transactions; for example, a loan by one business firm to another would be excluded. Also, only net increases in assets are treated as uses of funds. Debt repayment or dissaving, which are in fact uses of funds, are treated as negative sources of funds. In the same way, disinvestment in real assets or the sale of securities, which are in fact sources of funds, are treated as negative uses. This characteristic of the accounts facilities handling the data uniformly, but unfortunately it may also obscure some changes both within sectors and among different sectors. For a given sector, and by summing all sectors, for the economy as a while, the following equality is obtained:
Δ net worth + Δ liabilities = Δ real assets + Δ financial liabilities. (Δ denotes 'change')
Or,
saving + borrowing = investment + lending
It follows that if, in a particular sector, saving > investment, then lending > borrowing. This sector is a surplus sector and a net lender to other sectors. If investment > saving, then borrowing > lending. In this case the sector is a deficit sector and a net borrower from other sectors.
In principle, an account is easily established for each of the several sectors that make up the economic system. Sources and uses of funds are identified as in the case of our hypothetical sector. If we place these statements side by side, we form a matrix to describe an interconnected system of flow of funds for, say, a year. As is shown in the hypothetical matrix in Table 1.1, not only does each sector's source match its uses, but, by summation, total sources equal total uses. Furthermor whereas S ≠ I, for any sector individually, for the economy as a whole S=I.
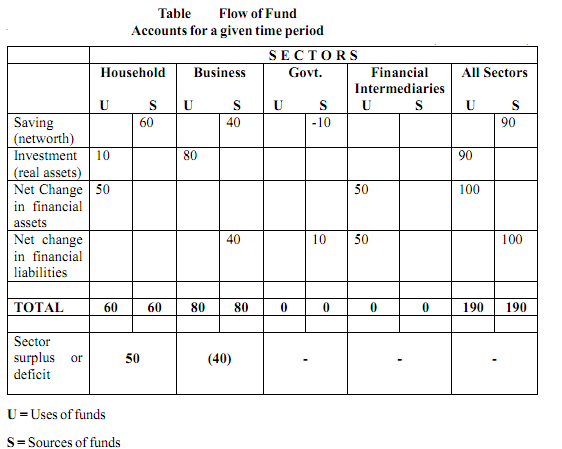
Table is a simplified, hypothetical flow of funds matrix for an economy that has been divided into fours sectors. Items in the cells of the matrix represent dolor flows that occurred during a period of time. In general, U stands for the uses of funds and represents acquisitions or additions to assets, while S stands for sources of funds and represents additions to liabilities or to net worth.