Moment Area Theorems:
From the above discussions about the consistent deformation method, it may be observed that for the solution of statically indeterminate structures, it is necessary to determine slopes and deflections at various points. One of the most convenient and versatile methods for this is based upon two theorems, which are known as the moment-area theorems. You know in which the elastic line (or elastic curve) is the changed shape of the structure after loading or support movements etc. The first moment area theorem is related to the change of slope of the elastic line between any two points. The second moment area theorem is associated to the distance between the tangents drawn to the elastic curve at two given points. In fact these are semi-geometrical methods and are explained below.
You know how to draw the bending moment (M) diagram for a beam. In a beam with variable moment of inertia (I) and modulus of elasticity (E), on division of M by EI at all points we can plot the so-called M/EI diagrams.
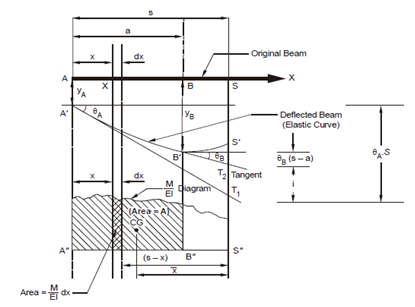
Let A and B be any two points on a beam ABS which when loaded shows a concave downward deflection A′B′ which is the elastic curve for this part of the beam. The tangents at A′ and B′ to this curve meet the vertical line SS′ at T1 and T2 respectively.