Comparison Of The Mechanics And Thermodynamic Concepts Of Energy
In mechanics, energy is stated as “the capacity for doing work”. This really symbolizes “mechanical energy”. It is not similar thing as the more comprehensive energy of thermodynamics, though the two ideas have many features in common. In advanced texts of thermodynamic, the capacity for work feature is related with the “quality” of energy. The illustration below illustrates the similarities and differences among the two notions.
The figure shown below illustrates a system including a hemispherical bowl and a steel ball. The ball is originally at rest at the lowest place of the bowl. It is then lifted by an external force until it is at rest close to the rim. For illustration, the ball could be lifted by hand and located at the higher position; or a magnet might be used to move the steel ball to the higher position. The work done by the system is negative in this procedure, as the surroundings have done work on the system. The heat transfer is absent, and therefore (E2 – E1) is positive; the energy of the system has risen. The “mechanical energy” has also raised, and by the similar amount; the ball has a higher potential energy.
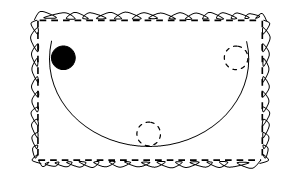
Figure: Hemispherical Bowl Containing a Steel Ball
The ball is now released and hence it rolls forwards and backwards within the bowl. There are neither heat nor work communications at the system boundary throughout the oscillations, and hence the energy of the system stays unchanged. When friction is absent, this is also true of the “mechanical energy”. Throughout the oscillations, the reduction of gravitational potential energy that the ball experiences in reaching the bottom of the bowl is precisely balanced by a rise in kinetic energy; the sum of the two energy terms stays constant.
When friction is present, though, the condition is very diverse. The height arrived at by the ball during each successive oscillation is decreased, and the maximum velocity achieved at the bottom of the bowl is also lower during each of the successive oscillation. Lastly, the ball comes to rest again at the bottom of the bowl. Again, as no heat or work interactions are present at the system boundary, the energy of the system has similar value as instantly after the ball was first raised (i.e., E2). The “mechanical energy” on the other hand, has reduced to the value accessible before the ball was increased (that is, E1).
In mechanics, it is described that “the energy has been dissipate”. Alternatively, it is assumed that “the energy has been transformed into heat”. Such axioms are not in accordance with the thermodynamic usage of the word “heat”. Even however the ball and the bowl are at higher temperature than in the starting, this has not taken place as an outcome of any heat transfer among the system and the surroundings.
The elucidation, according to thermodynamics, is that “mechanical energy has been converted into another mode of energy, known as internal energy”. Therefore the energy of thermodynamics involves the energy that is defined in mechanics, though is much more general, involving other forms of energy.