Regulation:
This synthesis of fatty acids takes place when carbohydrate and energy are plentiful and when fatty acids are scarce. The key enzyme in the regulation of fatty acid synthesis is acetyl CoA carboxylase that synthesizes malonyl CoA. This is a good instance of control at the committed step of a metabolic pathway. Acetyl CoA carboxylase is inactivated through the phosphorylation of a single serine residue through an AMP-activated protein kinase. Unlike cAMP- dependent protein kinase (protein kinase A) is kinase is not affected through cAMP, but instead is stimulated through AMP and inhibited through ATP. Therefore when the energy charge of the cell is low instance example there is a high AMP:ATP ratio fatty acid synthesis is switched off. Protein phosphatase 2A erased the phosphate set from inactivated acetyl CoA carboxylase shown in the figure, thereby reactivating it.
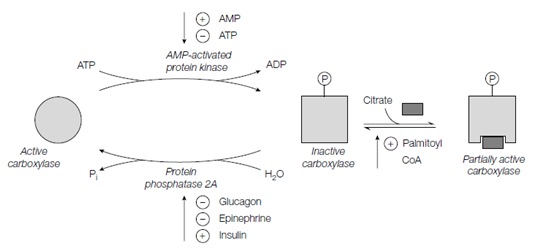
Figure: Summary of the control of acetyl CoA carboxylase by phosphorylation and allosteric regulation
Acetyl CoA carboxylase is also subject to hormonal regulation. When energy is needed, epinephrine and glucagon inhibit protein phosphatase 2A, therefore keeping acetyl CoA carboxylase in the inactive build and blocking fatty acid synthesis. Within the well-fed state when blood glucose levels are high and insulin stimulates acetyl CoA carboxylase, possibly through activating protein phosphatase 2A, thus leading to a raise in fatty acid synthesis. As well as its control through phosphorylation or dephosphorylation and acetyl CoA carboxylase is also allosterically regulated. The citric acid cycle intermediate citrate, the level of that is high when both acetyl CoA and ATP are abundant and allosterically stimulates acetyl CoA carboxylase. This conclusion in the conversion of the inactive phosphorylated form into a partially active form which is since phosphorylated, whereas activating fatty acid synthesis so which the excess acetyl CoA is 'stored' as fatty acid residues within triacylglycerol in adipose tissue. In compare, high levels of palmitoyl CoA, that is abundant when there is an excess of fatty acids and antagonize the effect of citrate on acetyl CoA carboxylase, reducing its activity and triggering off further fatty acid synthesis.