The pathway
The first committed step in fatty acid biosynthesis is the carboxylation of acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA using CO2 in the form of bicarbonate HCO3- . This reaction is catalyzed through the enzyme acetyl CoA carboxylase that has biotin as a prosthetic group, a general feature in CO2-binding enzymes. Single molecule of ATP is hydrolyzed in the reaction that is irreversible. The elongation phase of fatty acid synthesis all included intermediates linked to the terminal sulfhydryl group of the phosphopantetheine reactive unit in ACP; phosphopantetheine is also the reactive unit in CoA. Thus, the next steps are the formation of acetyl-ACP and malonyl-ACP through the enzymes acetyl transacylase and malonyl transacylase, respectively. (For the synthesis of fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms the three-carbon propionyl-ACP is the beginning point instead of malonyl-ACP.)
The elongation cycle of fatty acid synthesis has four stages for each round of synthesis. For the first round of synthesis these are:
1. Condensation of acetyl-ACP and malonyl-ACP to form acetoacetyl-ACP, releasing free ACP and CO2 (catalyzed by acyl-malonyl-ACP condensing enzyme).
2. Reduction of acetoacetyl-ACP to form D-3-hydroxybutyryl-ACP, by using NADPH as reductant (catalyzed by β-ketoacyl-ACP reductase).
3. Dehydration of D-3-hydroxybutyryl-ACP to produce crotonyl-ACP (catalyzed through 3-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase).
4. Reduction of crotonyl-ACP through a second NADPH molecule to give butyryl- ACP (catalyzed by enoyl-ACP reductase).
This first round of elongation generates the four-carbon butyryl-ACP. The cycle now replicate with malonyl-ACP adding two-carbon units in every cycle to the lengthening acyl-ACP chain. This process will continue until the 16-carbon palmitoyl- ACP is created. This molecule is not accepted through the acyl-malonyl-ACP condensing enzyme, and so cannot be elongated although through this procedure. Alternatively it is hydrolyzed through a thioesterase to provide palmitate and ACP.
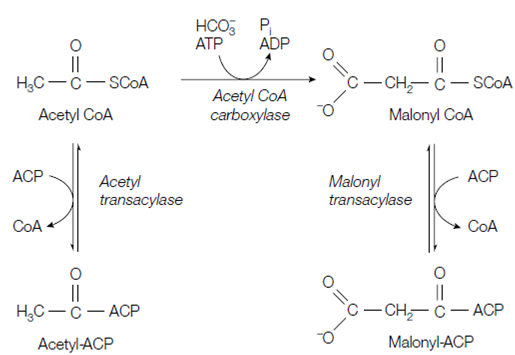
Figure: Formation of acetyl- and malonyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP).
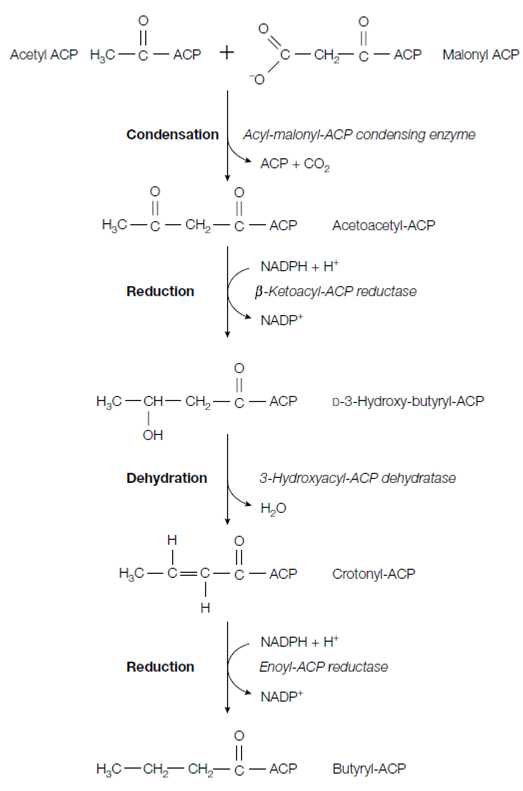
Figure: The elongation cycle of fatty acid synthesis.
The whole stoichiometry for the synthesis of palmitate is:
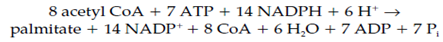
This is for each of the seven rounds of fatty acid elongation and one ATP is use in the synthesis of malonyl-CoA and two NADPH are used in the reduction reactions.
In eukaryotes the elongation of fatty acids beyond C16 palmitate is carried out by enzymes located on the cytosolic surface of the SER (smooth endoplasmic reticulum). Malonyl CoA is used as the two-carbon donor and the fatty acid is elongated as its CoA derivative rather than its ACP derivative.
In prokaryotes, every of the reactions of fatty acid synthesis are catalyzed through a separate enzyme. Moreover, in eukaryotes, the enzymes of the fatty acid synthesis elongation cycle are present in a single polypeptide chain and multifunctional enzyme complex, called as fatty acid synthase. A fatty acid synthase complex exists as a dimer and with the ACP moiety shuttling the fatty acyl chain among successive catalytic sites and from one subunit of the dimer to the other. It is, in effect, an extremely efficient production line for fatty acid biosynthesis