Transport into mitochondria:
Small- and medium-chain acyl CoA molecules (up to 10 carbon atoms) are readily able to cross the inner mitochondrial membrane through diffusion. Moreover, longer chain acyl CoAs do not readily cross the inner mitochondrial membrane, and needs a specific transport mechanism. To achieve this, the longer chain acyls CoAs are conjugated to the polar carnitine molecule that is found in both animals and plants. This reaction, catalyzed through an enzyme on the outer face of the inner mitochondrial membrane (carnitine acyltransferase I), erased the CoA set and substitutes it with a carnitine molecule shown in the figure. The acylcarnitine is then transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane through a carnitine or acylcarnitine translocase. This essential membrane transport protein transports acylcarnitine molecules into the mitochondrial matrix and free carnitine molecules out. At once inside the mitochondrial matrix the acyl
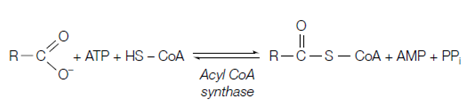
Figure: Activation of a fatty acid.
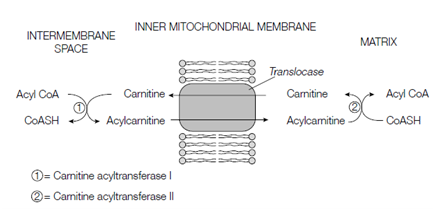
Figure: Transport of fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
set is transferred back on to CoA, releasing free carnitine, through the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase II that is situated on the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane show in the above figure.