Energy yield:
For each round of degradation, one NADH, one FADH2 and one acetyl CoA molecule are produced. Every NADH produces three ATP molecules, and every FADH2 generates two ATPs during oxidative phosphorylation. In addition, each acetyl CoA yields 12 ATPs on oxidation by the citric acid cycle. The total yield for each round of fatty acid degradation is there- fore 17 ATP molecules.
The complete degradation of palmitoyl CoA (C16:0) needs seven rounds of degradation and hence generates 7 x 5 = 35 ATP molecules. The total of eight acetyl CoA molecules are produced and therefore another 8 x 12= 96 ATP. Therefore the total ATP yield per molecule of palmitate degraded is 35 + 96 = 131 ATP. Moreover, one ATP is hydrolyzed to AMP and PPi in the activation of palmitate to palmitoyl CoA and resulting in two high-energy bonds being cleaved. Thus the net yield is 129 ATPs (Table 1).
The yield of ATP is decrease slightly for unsaturated fatty acids, because the additional metabolic reactions that enable them to be degraded through the β- oxidation pathway either included using NADPH or bypass an FADH2- generating reaction which is shown in the figure.
Ketone bodies When the stage of acetyl CoA from β-oxidation raise in excess of which required for entry into the citric acid cycle and the acetyl CoA is transformed into D-3-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate through a procedure called as ketogenesis. Acetoacetate D-3- hydroxybutyrate, and its nonenzymic breakdown product acetone are referred to collectively as ketone bodies.
Two molecules of acetyl CoA initially condense to form acetoacetyl CoA in a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the thiolysis step in β-oxidation. The acetoacetyl CoA acts with another molecule of acetyl CoA to form 3-hydroxy- 3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG CoA). this molecule is then cleaved to form acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. (HMG CoA is also the beginning point for cholesterol biosynthesis. The acetoacetate is then either reduced

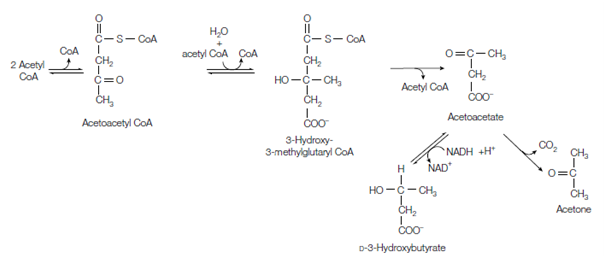
Figure: Conversion of acetyl CoA to the ketone bodies acetoacetate, acetone and D-3-hydroxybutyrate.
to D-3-hydroxybutyrate in the mitochondrial matrix or undergoes a slow for spontaneous decarboxylation to acetone. In diabetes, acetoacetate is generates faster than it can be metabolized. Therefore untreated diabetics have high stages of ketone bodies in their blood, and the smell of acetone can frequently be detected on their breath.
Acetoacetate and D-3-hydroxybutyrate are produced majorly in the liver and are not just degradation products of little physiological value. They are used in first choice to glucose as an energy source through certain tissues like as the kidney cortex and heart muscle. Therefore glucose is commonly the main fuel for the brain, under situations of starvation or diabetes this organ can switch to using predominantly acetoacetate.