Fatigue Mechanism
The scope of this text does not permit to discuss the exact mechanism of fatigue failure which lies in understanding the microscopic structure of material and defects at that level. Yet, it may be understood that final failure in fatigue is due to extension of a crack to critical value at which the uncracked portion is so small that specimen cannot sustain stress and hence fractures. This crack initiates from a microscopic area where stresses are high due to some metallurgical defect. Due to high stress at any point in a crystalline material, localised yielding will take place resulting into slip in the direction of maximum shearing stress. As the stress cycling continues, this slip-causes very minute cracks to generate and they keep on growing slowly and progressively with increasing number of cycles.
The progressive nature of crack propagation of fatigue is exhibited by the surface of fracture which has a very characteristics appearance. By just looking the fracture surface one can distinguish that the surface is divided into two regions – one smooth and other rough and jagged. The rough area is the one over which final fracture took place in stride manner. The smooth region is the one over which fatigue crack propagated slowly and progressively after its initiation. Because the two crack faces remain in contact and constantly rub against each other they become very smooth. If one examines the smooth zone very carefully under microscope, the point at which the crack initiated can be located and it is seen that marks like beach markings in form of conchoidal rings spread out from the point. These beach markings represent the sties where crack stopped momentarily. In many cases this nature of fatigue fracture surface can seen by just visual examination.
Under high power microscopes the region between two conchoidal rings has been examined to have similar rings and these are the sites where crack stopped after each cycle. The total number of cycles to failure as recorded has been found to coincide with the number of conchoidal marks.
Figure shows the characteristics fatigue fracture surface. The proportionate area of any one zone is indicative of level of stress. That is if smooth zone is much larger than rough zone it indicates that the stress level was low and vice-versa. If there are several points of crack initiation, it indicates that some geometrical stress concentration on the surface was present. In rotating bending the conchoidal rings tend to turn and centre on a different diameter. Figure (b) shows this tendency of crack to propagate in a direction opposite to that of rotation.
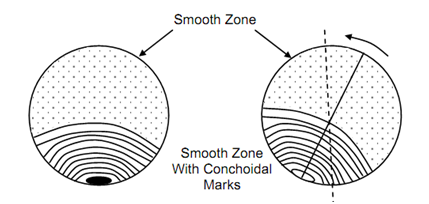
Figure: Smooth Zone with Conchoidal Marks