Negative Externalities:
Figure below shows the effects of a negative externality. For example, the steel industry is assumed to be selling in a competitive market - before pollution-control laws were imposed and enforced. The marginal private cost is less than the marginal social or public cost by the amount of the external cost, i.e., the cost of the smoking stacks and water pollution. This is represented by the vertical distance between the two supply curves. It is assumed that there are no external benefits, so that social benefit equals individual benefit.
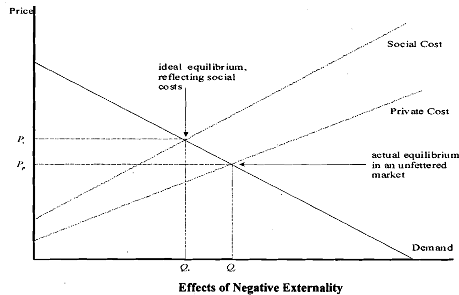
Supply and Demand with external costs:
If the consumers take into account their own private cost only, they will end up at price P, and quantity Q, instead of the more efficient price P, and quantity a. The latter price and quantity reflect the idea that the marginal social benefit should equal the marginal social cost, i.e., production should be increased only as long as the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost. The result in an unfettered market is ineficient since at the quantity Q, the social benefit is less than the societal cost, so society as a whole would be better off if the goods between Q and a had not been produced. The problem is that people are buying and consuming too much.
This discussion implies that pollution is a problem where the disjuncture between marginal and social costs that is not solved by the free market.