Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane envelops the cell and separating it from the external environment and maintaining the osmotic pressure and correct ionic composition of the cytosol. The plasma membrane, like all of the membranes, is impermeable to most substances but the presence of particular proteins in the membrane permits certain molecules to pass through, hence making it selectively permeable. The plasma membrane is also involved in communicating with other cells, in specific through the binding of ligands (small molecules such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and so on) to receptor proteins on its surface. Also the plasma membrane is involved in the exocytosis (secretion) and endocytosis (internalization) of proteins and other macromolecules.
(a)
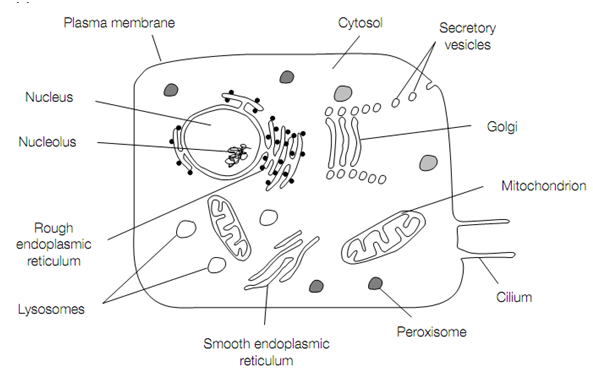
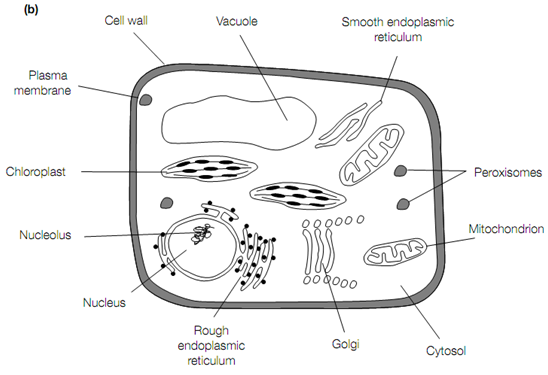
Eukaryote cell structure. (a) Structure of a typical animal cell, (b) structure of a typical plant cell.