Reactions of Ethers, Epoxides, and Thioethers:
Ethers
Ethers are usually unreactive functional groups and the only helpful reaction which they go through is cleavage through strong acids like HI and HBr to generate an alkyl halide and an alcohol.
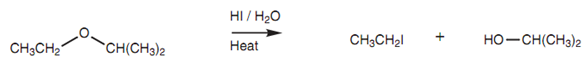
Figure: Cleavage of an ether to an alkyl halide and an alcohol.
The ether is very first protonated by the acid, then nucleophilic substitution occurs where the halide ion works like the nucleophile. Primary and secondary ethers react through the SN2 mechanism and the halide reacts at the least substituted carbon atom to generate an alkyl halide and an alcohol.
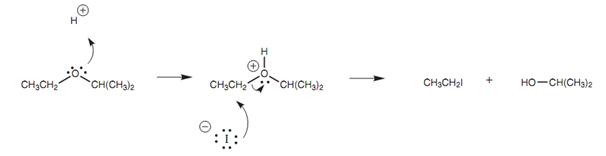
Figure: Mechanism for the cleavage of an ether.