Properties of Ethers, Epoxides and Thioethers:
Ethers
Ethers contain oxygen related to two carbon atoms by σ bonds. In aliphatic ethers (ROR), the three atoms included are sp3 hybridized and encompasses a bond angle of 112?. Aryl ethers are ethers in which the oxygen is related to one or two aromatic rings (ArOR or ArOAr) in which case the attached carbon(s) is sp2 hybridized.
The C-O bonds are polarized like that the oxygen is little negative and the carbons are slightly positive. Because of the slightly polar C-O bonds, ethers have a small dipole moment. Though, ethers have no X-H groups (X heteroatom) and cannot interact through hydrogen bonding. Hence, they have lower boiling points than comparable alcohols and identical boiling points to comparable alkanes. Though, hydrogen bonding is possible to protic solvents resultant in solubilities identical to alcohols of comparable molecular weight.
The ether's oxygen is a nucleophilic center and the neighboring carbons are electrophilic centers, but in both of the cases the nucleophilicity or electrophilicity is weak. Hence, ethers are comparatively unreactive.
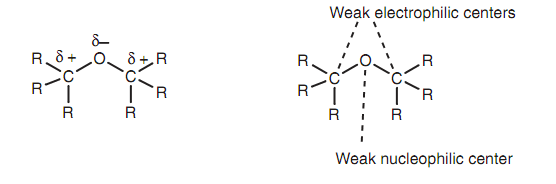
Figure: Properties of ethers.