Economic Advantages of Sub-central Governments:
It is generally opined that local governments performed more efficiently than a regional or state government and regional governments are more efficient than the federal or Central Government. But some people hold an opinion just opposite of it.
The fact is that some functions are more efficiently rendered by the local governments while some other functions are carried out by the Central or Federal government. Especially the local governments are more efficient in the provision of local public goods having a spatial or geographical limitation. This is mainly because the preferences of residents are likely to vary from one community or group to another. For example, a community which desires to have an effective police force rather than streetlights can have such services without an interference of the choice of the preferences of another community which wants to have an altogether different set of services. It implies that a federal system with its multi-levels of government contains greater efficiency than a unitary system where the same level of services are provided to all its citizens. In other words a federal structure with several sub-central governments will be able to provide a level of outputs that really corresponds to the preferences among different communities than a national and centralized government. Such an advantage of sub-central governments is illustrated in Figure. In the diagram output per person is represented on the x-axis and the number of people are represented on the y-axis. If there are three different communities A and B and C and a public good X, the diagram explains the optimal level of output of the public good. A1 A2, B1B2 and C1C2 curves show the preferred quantities of the public good X by therespective communities.
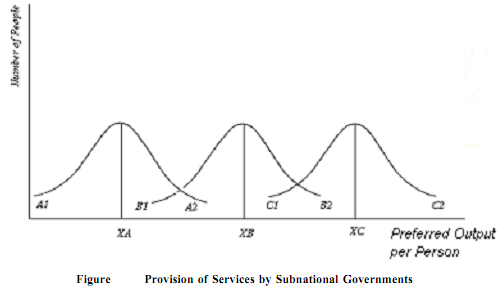
As may be observed from the diagram if a national government were to provide a uniform level of the public good X to all the existing communities, it would probably provide a medium level of XB which is very unsatisfactory to the residents of A and C Communities. On the other hand if there exists three independent governments, it results into three different levels of output XA, XB and XC. So the range of outputs provided by local governments is more efficient than a uniform level of output supplied by a national government. Of course, not all residents would be better off in such a situation. For example, the residents of communities whose preferences place them near A2 and C1 in the diagram are put to disadvantage when XA and XC outputs are provided respectively than XB. So in a federal context, people are free to shop around for a community whose tax and expenditure polices are best suited to their needs(Charles Tiebout). To elaborate, residents in Community A who choose XB more than XA can move from community A to Community B. As a result of consumer mobility induced by the process of consumers' choice of communities in response to differences in governmental services increases the efficiency advantages of sub- central governments. The second important advantage is that the local governments may be more responsive to the needs of its citizens. In other words, the political process required in smaller units of government is more efficient than in larger unit governments. It is widely believed that local governments are closer to the people and may possess fewer defects in the decision-making process as the role of pressure groups would be less. Moreover, the voters are more knowledgeable about how the tax money is spent.
Another advantage attributed to sub-central governments in a federal system is that scope for innovation and experimentation is larger. The sub-central governments in large numbers naturally will make experiments with new policies and the experimentation can be beneficial to other governments. If the policy experimented is successful, others will emulate and avoid implementation in case of a failure of the policy or service.
Though decentralization has several economic advantages in a federal economy, what is more important is the division of powers and functions among different levels of government and how the problems of efficiency and equity are resolved. Especially, it is necessary to know the role of the sub-central governments vis-à-vis the federal government in rendering the functions as well as powers. So let us discuss about the division of functions of allocation, distribution and stabilization among different layers of government in a federation.