Michaelis–Menten model
The following concept is used in the Michaelis–Menten model of enzyme catalysis:
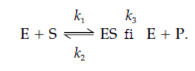
The enzyme which is denoted by E combines with its substrate that is denoted by S to form an enzyme–substrate complex that is denoted by ES. The ES complex can dissociate again to form E + S, or can go on chemically to form E and the product P. The rate constants k1, k2 and the k3 defines the rates related with each and every step of the catalytic procedure. It is supposed that there is no signi?cant rate for the backward reaction of enzyme and product (E + P) being converted to ES complex. [ES] leftovers approximately constant.
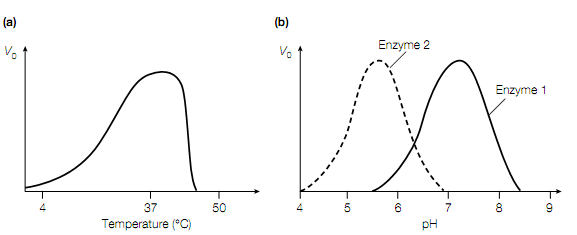
Figure: The effect of (a) temperature and (b) pH on enzyme activity.
until closely all the substrate is used, therefore the rate of synthesis of ES equals its rate of consumption over most of the course of the reaction; which is, ES maintains a steady state. From the observation of the properties of several enzymes it was known in which the initial velocity (V0) at low substrate concentrations is straightly proportional to [S] although at high substrate concentrations the velocity tends towards a maximum value, which is the rate becomes independent of [S]. This maximum velocity is known as Vmax the units of μmol min. The initial velocity (V0) is the velocity measured experimentally before more than approximately 10 percent of the substrate has been converted to product in order to minimize like complicating factors as the effects of reversible reactions inhibition of the enzyme through product and progressive inactivation of the enzyme.
Michaelis and Menten define an equation to describe these observations the Michaelis–Menten equation is given below:

This equation elaborates a hyperbolic curve of the kind described for the experimental data in Figure. In deriving the equation, Michaelis and Menten described Km a new constant the Michaelis constant units Molar instance for per mole.

Km is a measure of the stability of the ES complex being equal to the sum of the rates of breakdown of ES over its rate of formation. For several enzymes k2 is much greater than k3. In Under these circumstances Km becomes a measure of the af?nity of an enzyme for its substrate because its value depends on the relative values of k1, k2 for ES dissociation and formation, correspondingly. A high Km denotes weak substrate binding k2 predominant over k1, a low Km denotes strong substrate binding k1 predominant over k2. Km can be determined experimentally through the fact in which its value is equivalent to the substrate concentration at that the velocity is equal to half of Vmax.