Enzyme units
Enzyme activity may be described in a number of ways. The commonest is through the initial rate (V0) of the reaction being catalyzed for example μmol of substrate transformed per minute and μmol min 1). There are also two typical units of enzyme activity the enzyme unit which is denoted by U and the katal denoted by kat. An enzyme unit is which amount of enzyme that will catalyze the transformation of 1 μmol of substrate per minute at 25.C under finest conditions for that enzyme.
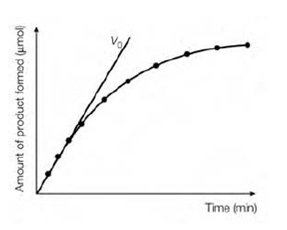
Figure: The relationship between product formation and time for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
The katal is the accepted SI unit of enzyme activity and is denoted as particularly that catalytic activity which will increase the rate of a reaction through one mole per second in a specified system. It is possible to convert among these variant units of activity using 1 μmol min-1 =1U =16.67 nanokat. The word activity or total activity refers to the total units of enzyme in the sample, while the specific activity is the number of enzyme units per milligram of protein that is units mg-1. The specific activity is a measure of the purity of an enzyme; in duration the purification of the enzyme its specific activity raise and becomes constant and maximal when the enzyme is pure.