Reversible noncompetitive inhibition
A noncompetitive inhibitor binds reversibly at a site other than the active site and causes a modification in the whole 3D shape of the enzyme which leads to a decrease in catalytic activity. Because the inhibitor binds at a various site from the substrate the enzyme should bind the inhibitor, the substrate or both the substrate and inhibitor together. The effects of a noncompetitive inhibitor cannot be overcome through increasing the substrate concentration so there is a reduction in Vmax. In noncompetitive inhibition the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate is not changed and so Km remains the similar. An instance of noncompetitive inhibition is the action of pepstatin on the enzyme renin.
Noncompetitive inhibition can be known on a Lineweaver–Burk plot because it increase the slope of the experimental line and alters the intercept on the y-axis because Vmax is decreased but leaves the intercept on the x-axis unchanged because Km remains constant.
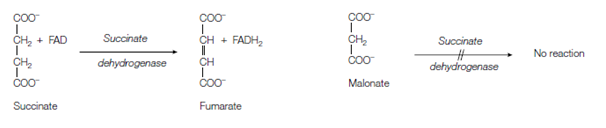
Figure Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate
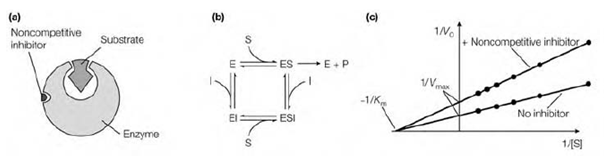
Figure: The characteristics of noncompetitive inhibition. (a) A noncompetitive inhibitor binds at a site distinct from the active site; (b) the enzyme can bind either substrate or the noncompetitive inhibitor or both; (c) Lineweaver-Burk plot showing the effect of a noncompetitive inhibitor on Km and Vmax.