Enolate ion:
Resonance structures present the great possibilities for a specific molecule and the true structure is actually a hybrid of both. The 'hybrid' structure depicts that the negative charge is 'smeared' or delocalized among three sp2 hybridized atoms.
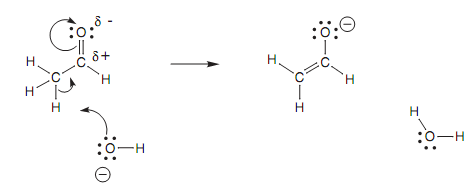
Figure: Mechanism for the formation of the enolate ion.
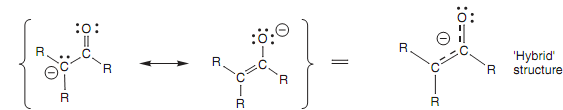
Figure: Resonance structures and 'hybrid' structure for the enolate ion.
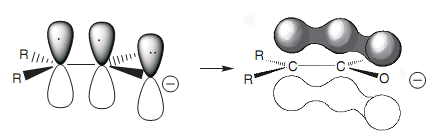
Figure: Interaction of 2p orbitals to form a molecular orbital.
Because these atoms are sp2 hybridized, they are planar and have a 2p orbital that can interact along with its neighbors to make one molecular orbital, so spreading the charge among the three atoms. Keep this in mind; it is possible to state which of the methyl hydrogens is veru much likely to be lost in the creation of an enolate ion. The hydrogen circled is the one that will be lost because the σ C-H bond is properly orientated to interact with the π orbital of the carbonyl bond. The orbital diagram demonstrates this interaction. A Newman diagram can as well be drawn through looking together the C-C bond to indicate the relative orientation of α hydrogen that will be lost. In this specific instance, there is no complexity in the proton being in the correct orientation because there is free rotation around the C-C single bond.