Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopy:
Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopy (CARS) is a technique that uses two lasers. One has a fixed frequency ν1 and the other could be tuned to a lower frequency ν2. While combined, these two lasers result in coherent radiation at a frequency equivalent to (ν = 2ν1 -ν2), besides a number of other frequencies. The energy changes during the CARS experiment are given in Figure.
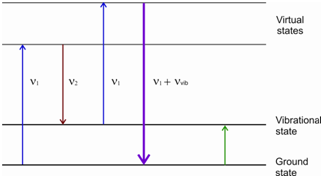
Figure: Schematic representation of the energy changes during the CARS experiment
Within CARS measurements two laser beams are passed by the sample and the second laser is tuned until it matches one of the Raman frequencies (sayν1 -ν vib).
Under like conditions the coherent emission would be at a frequency given through the following equation
ν = 2ν1 - (ν1 -ν vib ) = ν1 +ν vib
This, in fact, is the frequency of the corresponding anti-Stokes line; therefore the name. The schematic diagram of the experimental set up for the CARS experiment is given in Figure. The benefits of CARS spectrum is in which the Raman transitions in the presence of incoherent background radiations could also be studied.