Plastics, Reinforced Plastics And Adhesives
INTRODUCTION
Organic materials specifically that occur in nature like wood and leather have been utilized for engineering purposes. The modern developments where weight reduction, corrosion resistance, easy fabrication, and good appearance are being attained have focused attention on the materials called as plastics.
Plastic is utilized as a class name for a group of materials that might be formed or moulded into various shapes. Plastics are synthetic materials & chemically they still belong to larger group of materials called polymers.
Polymers are materials of complex nature having several units frequently joined in a chain as structure. The word mer in Greek means a unit. A monomer is a single unit. Many monomers join together to compose a polymer. As an instance one can consider a polymer called polyethylene in Figure.
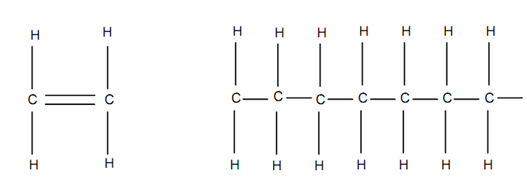
(a) Monomer (b) Polyethylene Chain Molecule
Figure: Polyethylene Polymer
In polyethylene, the unit that is repeated is C2H4 or ethylene.
Polymers are classified into three broad divisions, viz. fibres, plastics and elastomers.
We shall consider the properties and applications of plastics that have now become very commonly utilized engineering materials. Although much less in strength than metals, plastics are specifically preferred for their low density. Additionally various plastics might be machined simply, they have good surface finish & are not corroded in atmosphere. Plastics do not conduct electricity and therefore are used in domestic electrical fittings. They are enhancing being used for furniture, pipings , interiors of buildings, cars & aeroplanes. The mechanical strength of plastics is largely enhanced by reinforcing them with fibres which has given increase to a different class of materials called reinforced plastics. These materials have extremely good strength for low density. As early as in the year 1960 an average car utilized only 12 kgf of plastic which go up to 100 kgf in eighties and as much as to 150 kgf in nineties. Additionally, to above properties, removal of surface finishing, reduction of noise, ease of assembly, and vibration and low cost make them very popular in mechanical engineering applications.
Objectives
After learning this unit, you should be able to
- understand basic nature of plastics,
- distinguish among different types of plastics,
- understand polymerisation & its types,
- explain the term elastometer in a convenient way,
- understand the properties of plastic, its disadvantages and advantages,
- know the engineering plastics & their applications,
- appreciate the term reinforced plastic,
- list the different types of processes to built reinforced plastics,
- define adhesives,
- understand kind of adhesive and their applications, and
- have a brief of many design considerations relating to the plastic.