Units of Energy
There are many ways of measuring energy. We will talk about the ones relevant to our discussion. Most electrical appliances have a certain power rating, for example, a 60 W light bulb or a 1 kW room heater. It is, therefore, very common to measure electrical energy consumption in terms of power and time.
Power is the rate at which energy is used: Power = Energy / Time
or Energy = Power × Time
The unit of energy relevant for you at the moment is kilowatt-hour (kWh). It is the energy consumed in one hour through an electrical equipment of 1 kW (1000 W) rating. This is one unit of electrical energy measured through the meter.
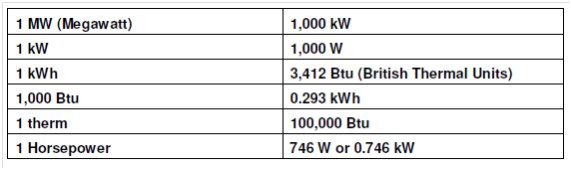
The usage of energy units varies from industry to industry and one equipment manufacturer to another. Table provides conversions of a few energy units.
Table: Conversion of Energy Units
Before we end from here, we would like to emphasize in which the term Energy Accounting applies to all forms of energy derived from several sources, e.g., from Other Fuels, Water, Natural Gas, Sewer, Solid Waste, etc. For instance, you could remain an account of your car petrol consumption and compare it with the standard consumption to establish the managed practice for your car.
Therefore, here we will focus on energy accounting for the electricity sector. We now introduce the concept of energy accounting.