Specific Internal Energy
The Potential and kinetic energy are macroscopic types of energy. They can be imagined in terms of the place and the velocity of objects. Additionally to these macroscopic types of energy, a substance possesses numerous microscopic kinds of energy. The microscopic forms of energy involve those due to the translation, rotation, vibration, and interactions amongst the molecules of a substance. No one of these kinds of energy can be measured or computed directly, though methods have been developed to compute the change in the total summation of all such microscopic kinds of energy. Such microscopic forms of energy are together termed as internal energy, customarily denoted by the symbol U. In engineering applications, the standard unit of internal energy is the British thermal unit (Btu) that is also the unit of heat.
The specific internal energy (u) of the substance is its internal energy per unit mass. This equivalent the total internal energy (U) divided by the total mass (m).
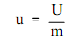
Here:
u = specific internal energy (Btu/lbm)
U = internal energy (Btu)
m = mass (lbm)