Affective basal ganglia circuit
The core of the limbic system consists of the affective striato-thalamo-cortical circuit and its connections with the amygdala. This is laid out in much the same pattern as the motor loop, which except the striatal part is the ventral striatum that are nucleus accumbens, nAc that projects to the ventral pallidum which is ventral part of the globus pallidus. The ventral pallidum relays by the mediodorsal thalamus to the anterior cingulate cortex and medial orbital prefrontal cortex. The loop is closed through connections from the cortex back to the nucleus accumbens. The reciprocal connections of the affective loop with the amygdala, that is responsible for fear learning and is modulated through the dopaminergic mesolimbic system that is concerned with reward learning.
Output of the nucleus accumbens goes to the compact component of the substantia nigra. This allows the activity of the cognitive and motor striato-thalamo-cortical circuits to be changed providing for some of the motor and the cognitive aspects of emotional states.
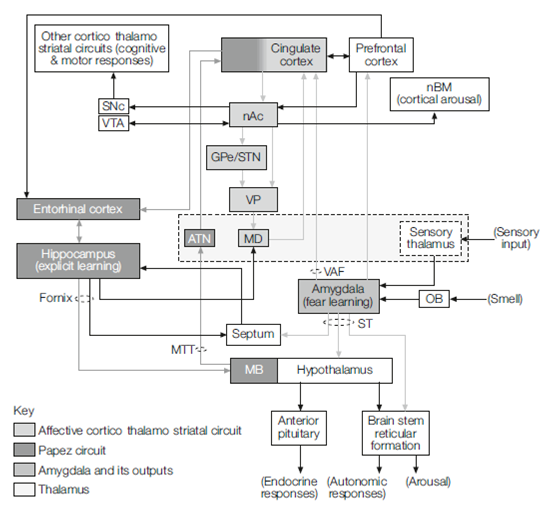
Figure: Circuitry implicated in emotions. MB, mammillary bodies; ATN, anterior thalamic nucleus; MD, mediodorsal nucleus; nAc, nucleus accumbens; GPe/STN, globus pallidus (external part)/subthalamic nucleus; VP, ventral pallidum; SNc, substantia nigra (compact part); VTA, ventral tegmental area; nBM, basal nucleus of Meynert; VAF, ventral amygdalofugal pathway; ST, stria terminalis; MTT, mammillothalamic tract; OB, olfactory bulb.