E1 Mechanism:
The E1 mechanism generally takes place when an alkyl halide is dissolved in a protic solvent in which the solvent can work as a non basic nucleophile. These are similar conditions for the SN1 reaction and thus both these reactions generally occur at the same time resultant in a mixture of products.
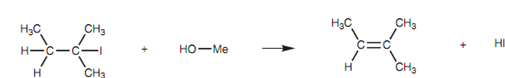
Figure: Elimination reaction of 2-iodo-2-methyl-butane.
As an instance of the E1 mechanism, we shall have a look at the reaction of 2-iodo-2-methylbutane with methanol displayed in figure.
There are 2 stages to this mechanism. The 1st stage is just the same process explained for the SN1 mechanism and that is cleavage of the C-X bond to make a planar carbocation intermediate in which the positive charge is stabilized via the three alkyl groups surrounding it. In the 2nd stage, the methanol makes a bond to the susceptible proton on the β-carbon.
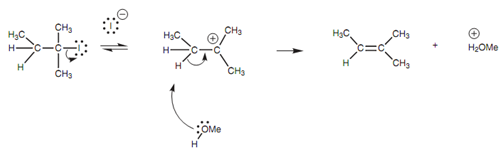
Figure: The E1 mechanism.
The C-H bond breaks and both electrons are employed to make a π bond to the neighboring carbocation. The 1st step of the reaction mechanism is the rate-determining step and because this is just only dependent upon the concentration of the alkyl halide, the reaction is ?rst order (El elimination ?rst order). There is no stereospeci?city included in this reaction and a mixture of isomers may be acquired with the more stable (more substituted) alkene being favored.