Calculations of Bearing and Included Angles:
Calculation of Included Angles
Having conducted the compass survey as elaborates previous, next step in plotting the survey results on maps is to calculate the included angle among two consecutive survey lines of the traverse.
(a) If the whole circle bearings of two lines at a station where these lines intersect are recorded, then the included angle between these lines would be equal to the difference between the whole circle bearings of two lines. If the difference is less than 180o the included angle would be interior angle and if it is more that 180o it will be the exterior angle between the two lines forming the traverse.
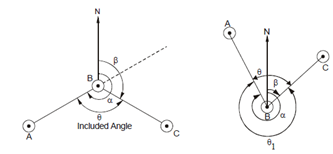
In Figure (a), it is given that back bearing (BB) of line AB, i.e. (α) = 240o and fore bearing (FB) of line BC, (β) = 120o. Then the included angle ABC, θ = α - β = 240o - 120o = 120o. Therefore, it can be said that if both the bearings are measured from a common point (B) then included angle can be obtained by subtracting FB of next line (BC) from the BB of previous line (AB).
In Figure (b), if α is given as 330o and β as 40o then θ1 = 330o - 40o = 290o is the exterior angle. In this case, included angle θ would be 360o - (difference between WCB of lines BA and BC).