Geiger-Muller Detector
A Geiger-Müller detector is a radiation detector that operates within the G-M region.
DESCRIBE the operation of a Geiger-Müller (G-M) detector to involve:
a. Radiation detection
b. Quenching
c. Positive ion sheath
The Geiger-Müller or G-M detector is a radiation detector which operates in Region V, or G-M region, as displays on Figure. G-M detectors generate larger pulses than other category of detectors. Therefore, discrimination is not possible, because the pulse height is independent of the category of radiation. Counting systems which use G-M detectors are not as complex as those by using ion proportional counters or chambers.
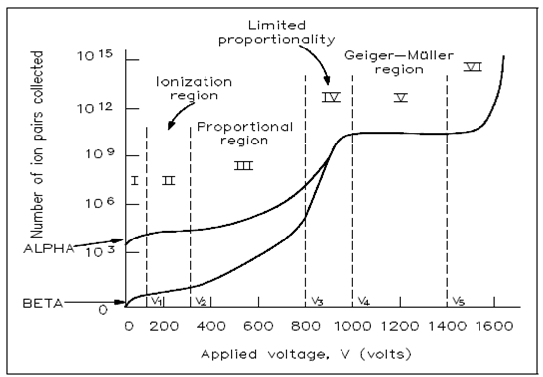
Figure: Gas Ionization Curve
The number of electrons collected through a gas-filled detector varies as applied voltage is increased. At one the voltage is raised beyond the proportional region, another flat portion of the curve is reached; this is called as the Geiger-Müller region. The Geiger-Müller region has two most important features:
1. The number of electrons generates is independent of applied voltage.
2. The number of electrons generates is independent of the number of electrons generates through the initial radiation.
This means in which the radiation producing one electron will have the similar size pulse as radiation producing hundreds or thousands of electrons. A purpose for these features is associated to the way in that electrons are collected.