Electroosmotic Flow:
While a high potential is applied across a capillary tube made of silica holding buffer solution, the positively-charged ions migrate towards the negative electrode and carry solvent molecules in the similar direction. As display in Figure, the electric double layer is established on the interface of silica and solution. The surface of the silicate glass capillary holds negatively-charged functional groups (create because
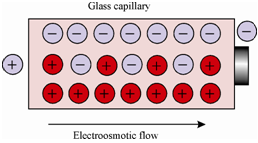
Figure: A charge distribution in capillary during electroosmotic flow
of the presence of Si-O-H ) and they attract positively charged counterions. This whole solvent movement is known as electroosmotic flow. During a separation, the uncharged molecules move at the similar velocity as the electroosmotic flow (with extremely little separation). A positively-charged ions move faster and negatively-charged ions move slower.