Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
Isoelectric concentration can be combined with SDS-PAGE to acquire very high resolution separations in a process which is known as two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Firstly the protein sample is subjected to isoelectric focusing in a narrow strip of gel containing polyampholytes. This isoelectric focusing gel strip is then placed on top of an SDS-polyacrylamide gel and electrophoresed to
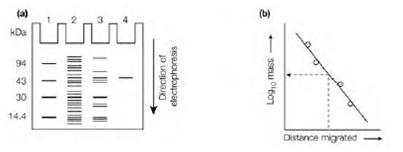
Figure: SDS-PAGE. (a) Appearance of proteins after electrophoresis on an SDS polyacrylamide gel. Lane 1, proteins (markers) of known molecular mass; lane 2, unpuri?ed mixture of proteins; lane 3, partially puri?ed protein; lane 4, protein puri?ed to apparent homogeneity; (b) determination of the molecular mass of an unknown protein by comparison of its electrophoretic mobility (distance migrated) with those of proteins (markers) of known molecular mass.
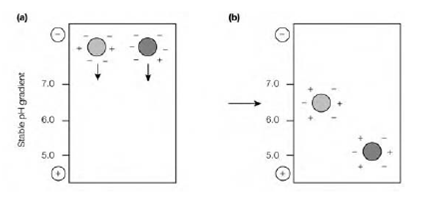
Figure: Isoelectric focusing. (a) Before applying an electric current. (b) After applying an electric current the proteins migrate to a position at which their net charge is zero (isoelectric point, pI).
generate a two-dimensional pattern of spots in that the proteins have been separated in the horizontal direction on the basis of their polyacrylamide and in the vertical direction on the basis of their mass. The whole result is in which proteins are separated both on the basis of their size and their charge. Therefore two proteins which have very same or identical polyacrylamides, and generate a single band through isoelectric focusing, if they have various molecular masses will produce two spots through two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Equally, proteins with same or identical molecular masses, that would produce a single band through SDS-PAGE, will also produce two spots if they have several polyacrylamides because of the initial separation via isoelectric focusing. The high resolution division of proteins in a complex mixture that can be achieved through two-dimensional gel electrophoresis makes this method extremely useful for comparing the proteome the entire complement of proteins in a organism or cell of cells or tissues under several conditions, example for differentiated versus undifferentiated cells and is frequently used prior to the analysis of individual protein spots through mass spectrometry .
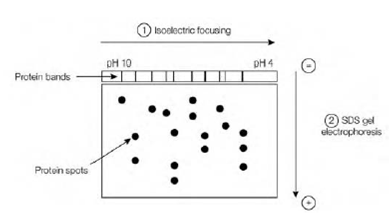
Fig: Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The protein sample is ?rst subjected to isoelectric focusing in one dimension and then to SDS-PAGE in the second dimension.