Reaction Profile:
Before describing the reasons behind the substituent effect, we have to refer the reaction profile of electrophilic substitution with the relative energies of starting material, intermediate, and product. The energy diagram that is shown below demonstrates the reaction pathway for the bromination of benzene.
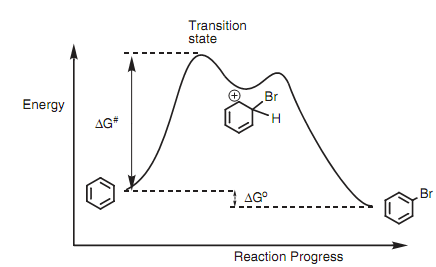
Figure: Energy diagram for electrophilic substitution.
The first stage in the mechanism is the rate-determining step and is the creation of the carbocation. This is endothermic and goes through a transition state that needs activation energy (?G#). The magnitude of ?G# ascertains the rate at which the reaction will take place and this in turn is determined through the stability of the transition state. The transition state resembles the carbocation intermediate and thus any factor that stabilizes the intermediate as well stabilizes the transition state and favors the reaction. Hence, in the discussions to follow we can regard as the stability of relative carbocations to ascertain which reaction is more favorable.