Deactivating groups - inductive m directing:
The alkyl groups are activating groups and they are direct substitution to the ortho, para positions. Electron withdrawing substituents as shown in the figure have the opposite effect. They deactivate the ring; form the ring less nucleophilic and less similarly to react with an electrophile. The electron-withdrawing effect as well destabilizes the reaction intermediate and creates the reaction harder. This destabilization is much more pronounced in the intermediates taking place from ortho/para attack and thus meta attack is favored.
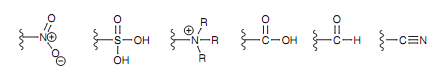
Figure: Examples of electron-withdrawing groups.
All of these groups comprise a positively charged atom or an electron deficient atom (that is an electrophilic center) straight attached to the aromatic ring. Because this atom is electron deficient, it encompasses an electron-withdrawing effect on the ring.