Addition of halogens:
There is no probability of dissimilar products while a halogen like bromine or chlorine is added to an unsymmetrical alkene. Though, this is not the case if water is employed as a solvent. In such types of cases, the halogen is attached to the least substituted carbon and the hydroxyl group is attached to the much more substituted carbon. This result can be described by proposing that the bromonium ion is not symmetrical and that even though the positive charge is shared among the bromine and the two carbon atoms, the positive charge is greater on the more substituted carbon as compared with the less substituted carbon.
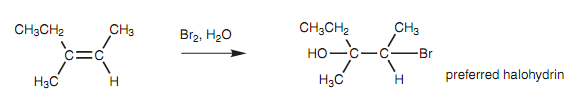
Figure: Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentene with bromine and water.