Mechanism for the electrophilic addition:
Similar mechanism explained above is followed in this reaction. Though, the first stage of the mechanism should include the nucleophilic alkene reacting along with an electrophilic centre, and yet there is no clear electrophilic center in bromine. The bond among the two bromine atoms is a covalent σ bond with both electrons evenly shared among the bromine atoms.
If there is no electrophilic center, how can a molecule such as bromine react with a nucleophilic alkene? The reply of this question lies in the fact that the bromine molecule approaches end-on to the alkene double bond and an electrophilic center is inducedshown in figure.
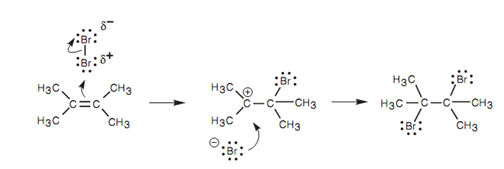
Figure: Mechanism for the electrophilic addition of Br2 with 2, 3-dimethyl-2-butene.
Because the alkene double bond is electron rich it repels the electrons in the bromine molecule and this results in a polarization of the Br-Br bond like that the nearer bromine becomes electron deficient (electrophilic). Now that an electrophilic center has been generated, the mechanism is similar like before.