Inverter:
An Inverter is a circuit which converts DC power into AC power. In the inverter, transistor is operated either in cut-off region or in saturated region. A typical transistor based on half bridge inverter consist of two series transistors connected across a center tapped DC supply as shown in Figure
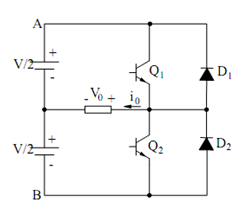
Figure (a) : Basic Inverter Circuit
The transistor operates in switching mode. Without base current, they operate in cut-off region and offer very high impedance so that current in the load is extremely small. While sufficient base current is applied, they operate in saturated region. In this case, voltage across the transistor is negligible and the current depends on the load impedance. Therefore, the two transistors are alternatively operated and each conducts for 1800 in each cycle. The various waveforms are illustrated in Figure (b).
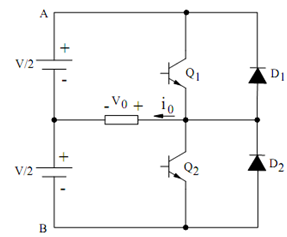
Figure (b) : Various Waveforms for the Inverter Circuit of Figure (a)
From Figure (b), it is seen that output voltage is equal to + V/2 during the positive half cycle and it becomes -V /2 during the next half.