Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Depending on the wavelengths, electromagnetic radiation is of many types and constitutes what is called an electromagnetic spectrum. The EM spectrum is divided into different regions on the basis of the methods required to generate and detect them. The radiations of different regions differ in terms of their features like energy, wavelength, etc. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into γ-rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, microwave and radio waves, etc. in terms of increasing wavelengths.
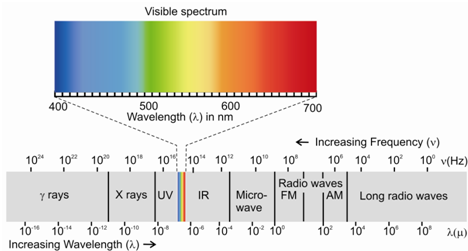
Figure: Electromagnetic spectrum showing different regions
The visible region of the spectrum which the human eye can sense is very tiny, as compared to the other spectral regions. Because the range of electromagnetic spectrum is quite huge, it is expressed within logarithmic or exponential scale.
The sources of radiation mostly give EM radiation spread over a range. In other words the EM radiation emitted by the source contains a number of radiations having slightly different wavelengths. For example, a hot deuterium lamp emits radiations in the wavelength range of approximately 190-380 nm. Such a radiation is called polychromatic radiation signifying that it consists of many radiations of different wavelengths. We could produce or separate out radiation of a single wavelength from the polychromatic radiation through using a suitable device called monochromator.