Classification And Relationships Of Electroanalytical Methods:
As we have seen there are a wide variety of electroanalytical methods available for the analytical purposes. A few of these techniques differ just in extremely few aspects but often the differences are important and require a good understanding of the techniques. For the most of methods discussed so far, we are interested in the relationships among four variables that are: emf, current, analyte concentration and time. Only exceptions to this are the conductometric techniques. Those methods are based on conductance of the solution. For the reason of categorization, these methods could be divided within interfacial methods and bulk methods, former are based upon phenomena that occur at the interface between electrode and solution and latter are based upon phenomena that occur in the bulk of the solution. Additional interfacial methods could be separated into main sub-group, static and dynamic, totally based upon whether electrochemical cells are operated within the absence or presence of current flow. Potentiometric and potentiometry titrations come under the category of static (zero current) methods. In dynamic interfacial methods current play important roles. These methods are additionally separated in various categories like voltammetry, coulometry amperometry, and electrogravimetry as display in Figure.
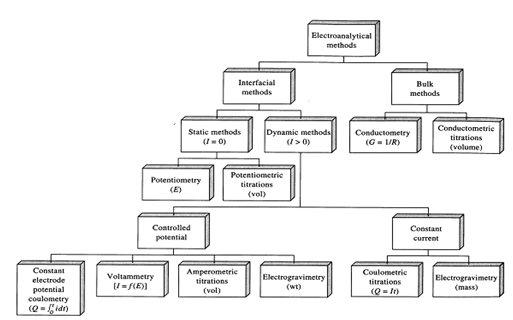
Figure: Classification of electroanalytical methods. Quantity measured is given in parentheses. Where I = current; E = potential; R = resistance; G = conductance; Q = quantity of charge, t = time; V = volume of a standard solution, m = mass of an electrolyte