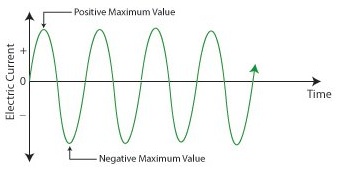
Alternating current:
In alternating current, the movement of charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in single direction.
The abbreviation AC is often used to mean simply alternating, as when they modify current or voltage.
AC is the type in which electric power is delivered to residences and businesses. The usual waveform of an AC circuit is a sine wave. In those applications, different waveforms are used, as like square waves or triangular waves. Radio and Audio signals carried on electrical wires are also type of alternating current. In these applications, main goal is frequently the recovery of information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal.